ASSESSMENT OF NATURAL AND ANTHROPOGENIC RISKS BASED ON A COMPLEX STUDY OF THE CITY OF BOLGAR AND THE DISTRICT
Keywords:
archaeology, cultural heritage, anthropogenic factor, exogenous processes, remote sensing, geoinformation systems, fortified settlements, Middle AgesAbstract
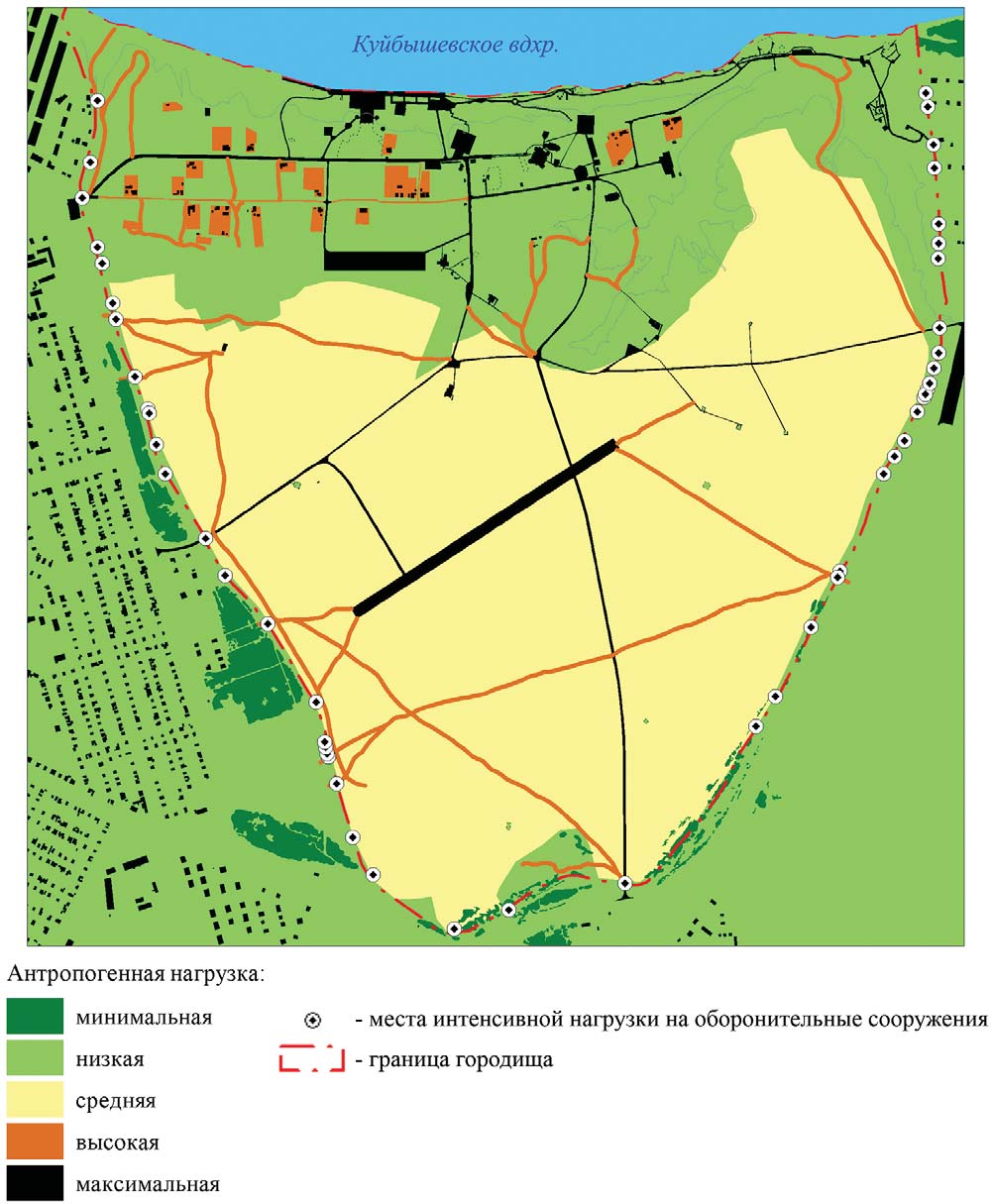
The scientifi c task of creating a system for assessment of cultural heritage object (monument of archaeology) territory state using both archaeological and geoecological research methods is being solved. A new method for assessing the risks of destruction of archeological monuments within the territory of the Bolgar fortifi ed settlement with the use of remote sensing methods, complex field studies and cartographic-geoinformation approaches to data processing is being developed. Modern instrumental methods were used to collect information on dangerous exogenous processes and anthropogenic impact within the monument territory. An analysis of the change in the functional use of the Bolgar settlement territory with the use of a multi-time aerial survey, was carried out. The results of the conducted studies are series of both inventory and evaluation maps, as well as recommendations for minimizing the impact on the archaeological heritage object under study. The obtained results will used to create a methodology for assessing the risks of destruction of archeological monuments.
References
Гайнуллин И.И., Дёмина Ю.В., Усманов Б.М. Опыт применения ГИС-технологий для оценки интенсивности разрушения археологических памятников в зоне влияния Куйбышевского Водохранилища // КСИА. № 226. 2012. С. 54−63.
Ландшафты Республики Татарстан. Региональный ландшафтно-экологический анализ / Под редакцией профессора О.П. Ермолаева. Казань: Слово, 2007. 411 с.
Asăndulesei A. Inside a Cucuteni Settlement: Remote Sensing Techniques for Documenting an Unexplored Eneolithic Site from Northeastern Romania // Remote Sensing. 9(1). 41. 2017. 22 p.
Campana S. Drones in aarchaeology. State-of-art and future perspectives // Archaeological Prospection. 24. 2017. p. 275−296.
Dubbini M., Curzio L.I., Campedelli A. Digital elevation models from unmanned aerial vehicle surveys for archaeological interpretation of terrain anomalies: Case study of the Roman castrum of Burnum (Croatia) // Journal of Archaeological Science. Reports 8. 2016, 121−134.
Esposito S., Fallavollita P., Melis M. G., Balsi M., Jankowski S. UAS imaging for archaeological survey and documentation // Proc. SPIE 8903. 2013.
Gaynullin I.I., Sitdikov A.G., Usmanov B.M. Abrasion processes of Kuibyshev Reservoir as a factor of destruction of archaeological site Ostolopovo (Tatarstan, Russia) // Advances in Environmental Biology. 8(4). 2014, 1027−1030.
Glossary of Environment Statistics, Studies in Methods / Series F. No. 67. United Nations. New York. 1997.
Nicu I.C. Natural hazards – a threat for immovable cultural heritage. A review // International Journal of Conservation Science 8(3) . 2017. pp. 375–388.
Romanescu G., Nicu I.C. Risk maps for gully erosion processes aff ecting archaeological sites in Moldavia, Romania // Zeitschrift für Geomorphologie. NF 58(4). 2014. pp. 509−523.
Wang J.–J. Flood risk maps to cultural heritage: Measures and process // Journal of Cultural Heritage. 16(2). 2015, 210−220.
Wu P–S., Hsieh C−M., Hsu M−F. Using heritage risk maps as an approach to estimating the threat to materials of traditional buildings in Tainan (Taiwan) // Journal of Cultural Heritage. 15(4). 2014, 441−447.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2018 I. I. Gainullin, B. M. Usmanov, P. V. Khomyakov

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







